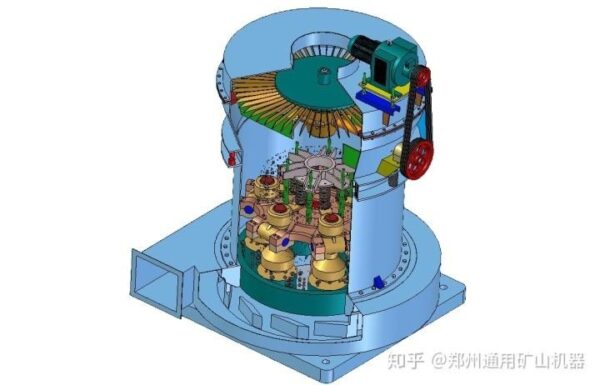
LCA
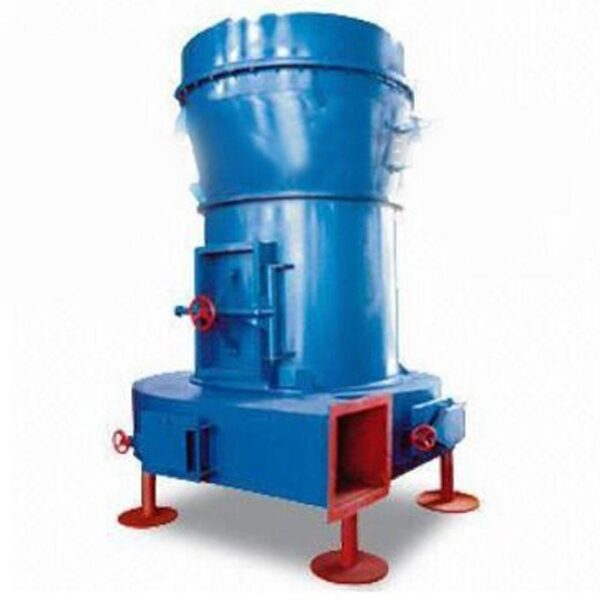
Raymond mill
Description
Raymond mill, also known as Raymond mill, is a commonly used grinding equipment, suitable for the preparation of various mineral powders and coal powders, such as fine powder processing of raw ore, gypsum ore, coal and other materials.
Working principle of Raymond mill
The grinding roller rolls tightly against the grinding ring under the action of centrifugal force. The scraper scoops up the material and sends it to the middle of the grinding roller and grinding ring. The material is crushed into powder under the action of the grinding pressure. Then, the fan blows the powdered material up and passes it through the analyzer. The material that meets the fineness requirement passes through the analyzer, and the material that does not meet the requirement returns to the grinding chamber for further grinding. The material that passes the analyzer is separated and collected in the cyclone separator. The exhaust air is isolated by industrial filter cloth and the exhaust is pulverized once.
Advantages of Raymond Mill
- The entire Raymond mill is a vertical structure with a relatively small footprint and strong systematization. It can form a complete production system from the rough processing of raw materials to transportation, powder making and final packaging.
- Compared with other grinding equipment, Raymond mill has a high screening rate, which is as high as99% , which is generally not achieved by other grinding equipment.
- The main transmission device of Raymond mill adopts closed gear box and pulley, which ensures smooth transmission and reliable operation.
- The important components of Raymond mill are made of high-grade castings and profiles. The fine workmanship and rigorous process ensure the durability of the whole set of equipment.
- The electrical system of the Raymond mill adopts centralized control, the grinding workshop can basically achieve unmanned operation and is easy to maintain.
Raymond mill uses and application scope:
Raymond mill is mainly suitable for grinding and crushing conventional materials, such as barite, calcite, potassium feldspar, talc, marble, limestone, dolomite, fluorite, lime, activated clay, activated carbon, bentonite, kaolin, cement, phosphate rock, gypsum, glass, manganese ore, iron ore, copper ore, chromium ore, refractory materials, thermal insulation materials, coal coke, coal powder, carbon black, clay, bone meal, titanium dioxide, iron oxide, quartz and other non-flammable and explosive materials with a Mohs hardness of no more than 7 and a humidity of less than 6% in the mining, chemical, construction and other industries. The particle size of the finished product can be adjusted arbitrarily within the range of 80-325 mesh, and the fineness of some materials can reach 600 mesh.